Earthquakes
First of all I think we should know what an earthquake is. An earthquake is shaking of the ground that is continuous. Earthquakes stop when there isn't enough energy to keep them going. The energy released by the sliding fault needs to be enough to overcome the friction holding the rocks in place. Once the earthquake comes up against too much friction, it will stop.
How do Earthquakes occur?

Earthquakes do we really know how they occur? Well now you can learn all that now. Earthquakes are caused by an abrupt shift of rock along a fracture of the earth called "Faults".
How Earthquakes are measured

Seismographs:When an earthquake occurs we wonder how do you get the magnitude for the earthquake? A seismograph is the device that scientists use to measure earthquakes. The goal of a seismograph is to accurately record the motion of the ground during a quake. If you live in a city, you may have noticed that buildings sometimes shake when a big truck or a subway train rolls by. The main problem that must be solved in creating is that when the ground shakes, so does the instrument. But most seismographs involve a large mass of a sort.
Richter Scale: The Richter magnitude scale was developed in 1935 by Charles Richter. Richter of the California institute of Technology as a mathematical device to compare the size of earthquakes. The magnitude of an earthquake is determined from the logarithm of the amplitude of waves recorded by seismographs. On the Richter Scale, magnitude is expressed in whole numbers and decimal fractions.
Richter Scale: The Richter magnitude scale was developed in 1935 by Charles Richter. Richter of the California institute of Technology as a mathematical device to compare the size of earthquakes. The magnitude of an earthquake is determined from the logarithm of the amplitude of waves recorded by seismographs. On the Richter Scale, magnitude is expressed in whole numbers and decimal fractions.
Seismic Waves
Primary Waves
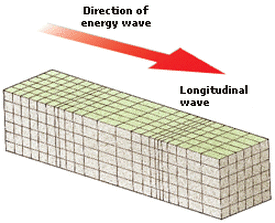
The primary waves are the fastest waves out of the three. This wave passes through solids, liquids and gases. The vibration of this wave is weak (only a slight vibration). Primary wave or P-waves can't go through shadow zones. Primary waves travel through rock, while they travel through rock tiny rock particles move back and forth, pushing them apart and going back together (in the direction the wave is traveling).
Secondary Waves
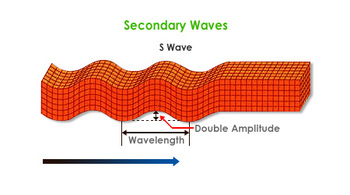
Secondary Waves only can pass through solids but cannot pass through liquids. A secondary wave is an earthquake wave in which rock particles at right angles to the direction the wave is traveling. This wave is the second fastest traveling wave out of the three seismic waves.
Surface Waves
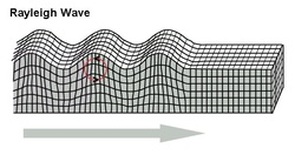
Surface Waves cause the most damage in during earthquakes. Surface waves only travel through the crust. Surface waves are easily identified on the seismographs when an earthquake occurs. The damage and the strength of the surface waves are reduced deeper in earthquakes. Surface Waves are also known as a "Rayleigh Wave" because ,the Rayleigh wave, named for John William Strutt, Lord Rayleigh, who had an mathematically had predicted the existence of this kind wave in 1885. A Rayleigh wave rolls along the ground just like a wave rolls across a lake or an ocean.
Faults
Normal Fault
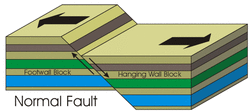
Normal Faults occur in divergent boundaries, one plate slides down. They are normally found in places where the lithosphere is stretched or at the edge of huge slumps and slides. When on slides down they move apart (for example, divergence or divergent boundary).
Reverse Fault
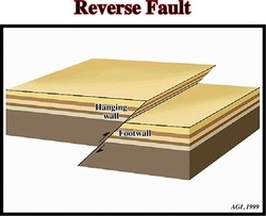
Reverse Faults occur in convergent boundaries, one plate slides up.Reverse faults are exactly the opposite of normal faults. If the hanging wall rises relative to the footwall, you have a reverse fault. Reverse faults occur in areas undergoing compression (squishing). If you imagine undoing the motion of a reverse fault, you will undo the compression and thus lengthen the horizontal distance between two points on either side of the fault.
Strike Slip Fault (Transform Fault)
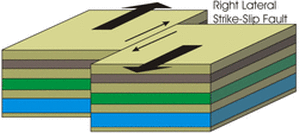
The Strike Slip Fault or the transform fault causes earthquakes by slipping. This fault line occurs in Transform Boundaries, they are also very similar to transform boundaries. The strike slip fault is the crust that moves past each other that also does have energy to make them snap in the end of the tension (stretching or straining).
